# Admin Service
Start the admin service:
web.BConfig.Listen.EnableAdmin = true
And you can specify the admin service host and port:
web.BConfig.Listen.AdminAddr = "localhost"
web.BConfig.Listen.AdminPort = 8088
Open this URL in web browser: http://localhost:8088/. Now you can see Welcome to Admin Dashboard.
# Statistics
Access http://localhost:8088/qps:
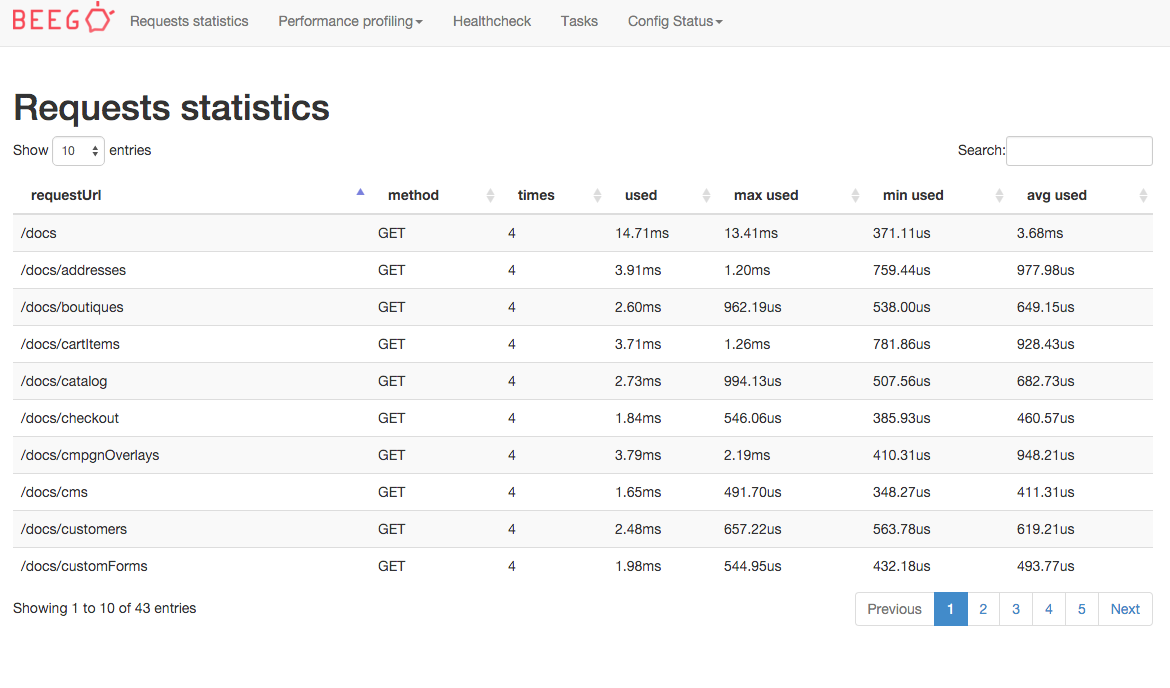
How can I use the statistics? Add statistics like this:
admin.StatisticsMap.AddStatistics("POST", "/api/user", "&admin.user", time.Duration(2000))
admin.StatisticsMap.AddStatistics("POST", "/api/user", "&admin.user", time.Duration(120000))
admin.StatisticsMap.AddStatistics("GET", "/api/user", "&admin.user", time.Duration(13000))
admin.StatisticsMap.AddStatistics("POST", "/api/admin", "&admin.user", time.Duration(14000))
admin.StatisticsMap.AddStatistics("POST", "/api/user/astaxie", "&admin.user", time.Duration(12000))
admin.StatisticsMap.AddStatistics("POST", "/api/user/xiemengjun", "&admin.user", time.Duration(13000))
admin.StatisticsMap.AddStatistics("DELETE", "/api/user", "&admin.user", time.Duration(1400))
Get statistics information:
admin.StatisticsMap.GetMap(os.Stdout)
Here is the output:
| requestUrl | method | times | used | max used | min used | avg used |
| /api/user | POST | 2 | 122.00us | 120.00us | 2.00us | 61.00us |
| /api/user | GET | 1 | 13.00us | 13.00us | 13.00us | 13.00us |
| /api/user | DELETE | 1 | 1.40us | 1.40us | 1.40us | 1.40us |
| /api/admin | POST | 1 | 14.00us | 14.00us | 14.00us | 14.00us |
| /api/user/astaxie | POST | 1 | 12.00us | 12.00us | 12.00us | 12.00us |
| /api/user/xiemengjun | POST | 1 | 13.00us | 13.00us | 13.00us | 13.00us |
# Profiling
Monitoring the performance of running processes is a very good way to optimize performance and to look for issues in our application. E.g.: information of GC and goroutine.
Profile provides a easy entry point for you to debug the application. It uses the ProcessInput entry function to process the requests. Here are some debugging types:
lookup goroutine
Print out the tasks of all goroutines which are currently running. You can easily see what all goroutines are doing.
goroutine 3 [running]:
runtime/pprof.writeGoroutineStacks(0x634238, 0xc210000008, 0x62b000, 0xd200000000000000)
/Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/pprof/pprof.go:511 +0x7c
runtime/pprof.writeGoroutine(0x634238, 0xc210000008, 0x2, 0xd2676410957b30fd, 0xae98)
/Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/pprof/pprof.go:500 +0x3c
runtime/pprof.(*Profile).WriteTo(0x52ebe0, 0x634238, 0xc210000008, 0x2, 0x1, ...)
/Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/pprof/pprof.go:229 +0xb4
_/Users/astaxie/github/beego/toolbox.ProcessInput(0x2c89f0, 0x10, 0x634238, 0xc210000008)
/Users/astaxie/github/beego/toolbox/profile.go:26 +0x256
_/Users/astaxie/github/beego/toolbox.TestProcessInput(0xc21004e090)
/Users/astaxie/github/beego/toolbox/profile_test.go:9 +0x5a
testing.tRunner(0xc21004e090, 0x532320)
/Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/testing/testing.go:391 +0x8b
created by testing.RunTests
/Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/testing/testing.go:471 +0x8b2
goroutine 1 [chan receive]:
testing.RunTests(0x315668, 0x532320, 0x4, 0x4, 0x1)
/Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/testing/testing.go:472 +0x8d5
testing.Main(0x315668, 0x532320, 0x4, 0x4, 0x537700, ...)
/Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/testing/testing.go:403 +0x84
main.main()
_/Users/astaxie/github/beego/toolbox/_test/_testmain.go:53 +0x9c
lookup heap
Print out information of current heap:
heap profile: 1: 288 [2: 296] @ heap/1048576
1: 288 [2: 296] @
runtime.MemStats
Alloc = 275504
TotalAlloc = 275512
Sys = 4069608
Lookups = 5
Mallocs = 469
Frees = 1
HeapAlloc = 275504
HeapSys = 1048576
HeapIdle = 647168
HeapInuse = 401408
HeapReleased = 0
HeapObjects = 468
Stack = 24576 / 131072
MSpan = 4472 / 16384
MCache = 1504 / 16384
BuckHashSys = 1476472
NextGC = 342976
PauseNs = [370712 77378 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
NumGC = 2
EnableGC = true
DebugGC = false
lookup threadcreate
Print out information of threads:
threadcreate profile: total 4
1 @ 0x17f68 0x183c7 0x186a8 0x188cc 0x19ca9 0xcf41 0x139a3 0x196c0
0x183c7 newm+0x27 /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:896
0x186a8 startm+0xb8 /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:974
0x188cc handoffp+0x1ac /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:992
0x19ca9 runtime.entersyscallblock+0x129 /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:1514
0xcf41 runtime.notetsleepg+0x71 /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/lock_sema.c:253
0x139a3 runtime.MHeap_Scavenger+0xa3 /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/mheap.c:463
1 @ 0x17f68 0x183c7 0x186a8 0x188cc 0x189c3 0x1969b 0x2618b
0x183c7 newm+0x27 /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:896
0x186a8 startm+0xb8 /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:974
0x188cc handoffp+0x1ac /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:992
0x189c3 stoplockedm+0x83 /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:1049
0x1969b runtime.gosched0+0x8b /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:1382
0x2618b runtime.mcall+0x4b /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/asm_amd64.s:178
1 @ 0x17f68 0x183c7 0x170bc 0x196c0
0x183c7 newm+0x27 /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:896
0x170bc runtime.main+0x3c /Users/astaxie/go/src/pkg/runtime/proc.c:191
1 @
lookup block
Print out information of block:
--- contention:
cycles/second=2294781025
start cpuprof
Start recording cpuprof info into created file cpu-pid.pprof.
stop cpuprof
Stop recording.
get memprof
Start recording memprof into created file mem-pid.memprof
gc summary
Check GC status:
NumGC:2 Pause:54.54us Pause(Avg):170.82us Overhead:177.49% Alloc:248.97K Sys:3.88M Alloc(Rate):1.23G/s Histogram:287.09us 287.09us 287.09us
# Health Check
It can check the health status of your application. E.g.: To check if database is available:
type DatabaseCheck struct {
}
func (dc *DatabaseCheck) Check() error {
if dc.isConnected() {
return nil
} else {
return errors.New("can't connect database")
}
}
Then you can add it as a check item:
admin.AddHealthCheck("database",&DatabaseCheck{})
After this you can send get request to /healthcheck:
$ curl http://beego.vip:8088/healthcheck
* deadlocks: OK
* database: OK
It will return the database status accordingly.
# Timed Tasks
The user needs to have added Timed Tasks to the application in order to perform the corresponding task checks and manually triggered tasks.
http://localhost:8088/task- or:
http://localhost:8088/task?taskname=task name
# Configuration information
- All configuration
http://localhost:8088/listconf?command=conf - Routers:
http://localhost:8088/listconf?command=router - Filters:
http://localhost:8088/listconf?command=filter
← Error Handling XSRF →